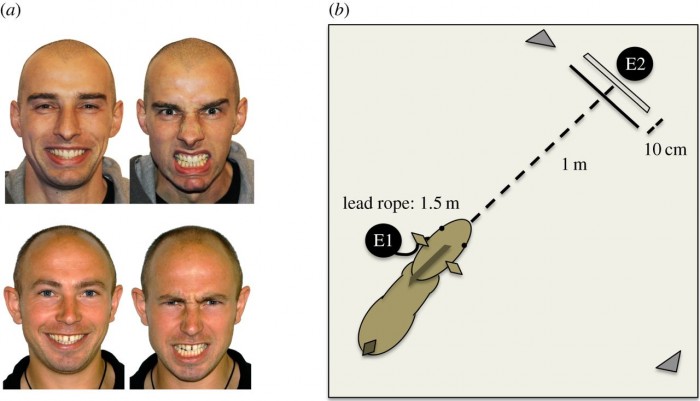
Horses respond to human facial expressions of emotion
Photographs of male's with a positive (happy) and a neagtive (angry) face where used in this study. The results showed that looking at the angry faces horses displayed a left-gaze bias (a lateralization generally associated with stimuli perceived as negative) and a quicker increase in heart rate (HR) towards these photographs. HR measures have the potential to provide objective insights into an animal's perception of external stimuli. In horses, HR correlates with behavioural indices of stress and fluctuates according to handler stress, demonstrating a potential physiological sensitivity to human affect.
In many social species, emotions provide valuable social and environmental information and are likely to play a key role in facilitating group cohesion and functioning. Positive emotion elicits behaviour towards rewarding stimuli, while negative emotions promote avoidance of possible threats, responsiveness to emotion in others is potentially highly adaptive.
Perception of emotion across species may be challenging where considerable morphological variation divides signaller and receiver.
Horses are an ideal model for research into interspecific communication of emotion, because they are able to both produce complex facial expressions and perceive these in conspecifics, as well as being sensitive to human-given signals including facial cues. The behavioural and physiological results reported here support the hypothesis that horses are able to recognize and respond in a functionally relevant way to heterospecific (human) facial expressions of anger.
> From: Smith et al., Biology letters 12 (2016) -. All rights reserved to The Authors. Click here for the online summary.